Drag the Labels to Identify Types of Fractures.
Check a answer for each of the three definitions all but one should be selected 1. Transverse fractures form perpendicular to the long axis of a bone and are the result of a force applied at a right angle to the bone.
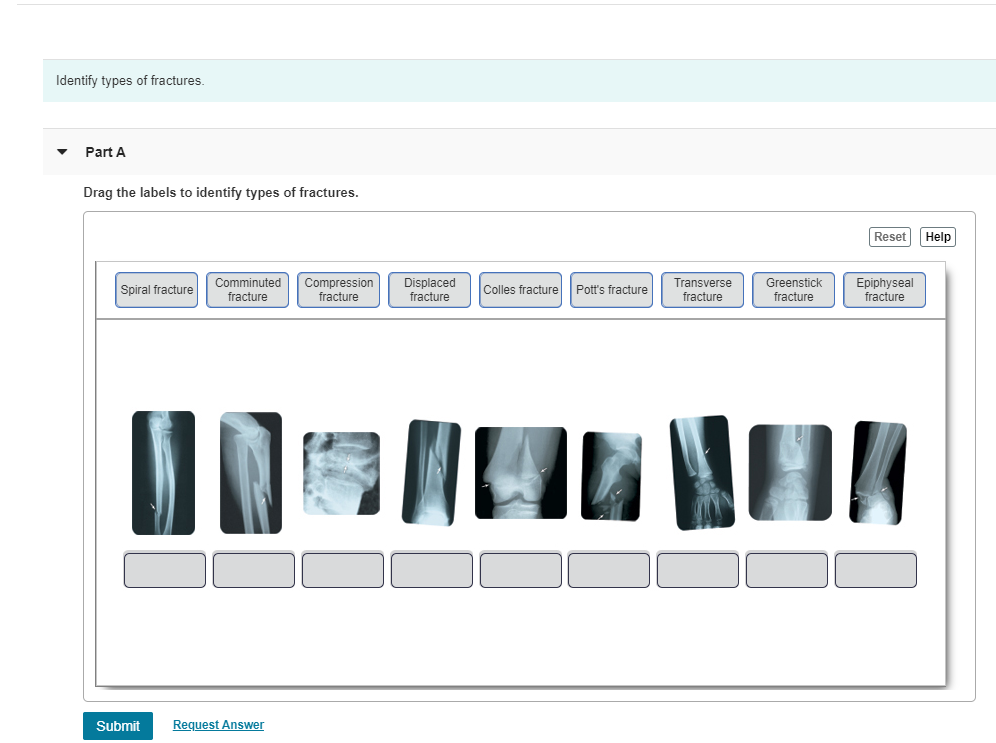
Solved Identify Types Of Fractures Part A Drag The Labels Chegg Com
This is a highly complicated injury and usually heals quite slowly.

. The patellae singular patella are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the cranial bones and sutures posterior view of the sk. Avulsion fractures are those which occur when a bone fragment from the main bone at a site of a ligament attachment to a joint breaks.
The break is parallel to the bones long axis. The picture below represents which are more likely to be eroded and which are less. One part of the bone has been twisted at the break point.
Drag the Labels to Identify Types of Fractures. The break has a curved or sloped pattern. Compare healthy bone with different types of fractures.
Spiral fractures result when excessive torsion or twisting force is applied to a limb fracturing the bone. If you want to redo an answer click on the box and the answer will go back to the top so you can move it to another box. Very large blunt irregularly shaped process3.
Other Apps - April 21 2022 Pelvic Fractures Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Post a Comment Read more Download Lagu Sheila Iklim. Three types of fracture. Predominantly occur in children.
And those rocks that are weak contains pores spaces and. Fractures can be separated into shear fractures slip surfaces and opening or extension fractures joints fissures and veins. Joints are usually planar features so their orientation can be described as a strike and dip.
A fracture that looks like a spiral staircase. The bony expansion carried on a narrow neck. Bone segments are pulled apart as a result of a twisting motion.
You have this type of fracture when the break is parallel to the long axis of the bone. Describe the timing of bone fracture for these long bones. A fracture oriented obliquely across the bone.
Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet hands and knees. Fracture does not cross the bone completely. Fractures are very narrow zones often thought.
Labeling the bones and synovial joints of the body by looking at the image and providing the bone AND synovial joint type for each number. A fracture perpendicular to the axis of the bone. Transform faults are strike-slip faults.
The orientation of various fracture types with respect to the principal stresses. The bone will be broken into several fragments. Table 61 reviews bone classifications with their associated features functions and examples.
Place the major steps in the repair of a fracture in order. Word bank is below image. Occurs straight across the long axis of the bone.
On strike-slip faults the motion is typically only horizontal or with a very small vertical component and as discussed above the sense of motion can be right lateral the far side moves to the right as in Figures 1212 and 1213 or it can be left lateral the far side moves to the left. Rocks that are comprised of resistant minerals like quartz prevailing in a moderately dry environment and which lacks in fractures and pores are least prone to weatheringFor example quartzite. Drag each label into the proper position to identify the type of bone cell described.
In addition closing or contraction fractures can be defined. The fracture is of the concave surface. Longitudinal fractures occur when the bone breaks along a vertical axis in a parallel path through the bone.
Which came first the bone or the cartilage. Two major types of more or less planar fractures can occur. Caused by a disease that weakens the bones.
Drag and drop the labels to describe the formation of either the fibrocartilage or bony callus during fracture repair. Not all childhood fractures are incomplete. Transverse fracture Spiral fracture Epiphyseal fracture Compression fracture Comminuted fracture Colles fracture Displaced fracture Potts fracture Greenstick fracture.
The whole cortex is not broken. Several breaks result in many small pieces between two large segments. Drag the correct description under each cell structure to identify the role it plays in the cell.
The fracture is on the convex surface. Types of Fractures Table 64 Type of fracture Description. Spiral fractures are the result of an extreme twisting force being exerted on a bone.
Oblique fractures are slanted fractures that occur when a force is applied at any angle other than a right angle to the bone. Carbon colorred2 This atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon d.
Part a animal cell structure drag the labels onto. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of the cell. Occurs at an angle that is not 90 degrees.
A closed fracture b open fracture c transverse fracture d spiral fracture e comminuted fracture f impacted fracture g greenstick fracture and h oblique fracture. Among all different types of fractures comminuted fracture is a serious one. Part D - Bone Growth Fractures and Remodeling Part of the process of fracture repair is the formation of a fibrocartilage callus and a bony callus.
More than 2 parts to the fracture. A fracture in more than two bits. As we learned in our discussion of physical weathering joints are fractures in rock that show no slippage or offset along the fracture.
This problem has been solved. The long bone has been bent.



No comments for "Drag the Labels to Identify Types of Fractures."
Post a Comment